|
Exact Audio Copy will then create the offset test CD. This writing process
takes a few minutes and a progress bar is indicating the status.
When this is finished it is time to perform a new read offset
detection with this offset test CD. Therefore eject the CD and insert it in the
drive of which you detected the read offset
earlier on this page. If this is the very same drive you just used to write the
CD with it is still recommended to open and close the drive's tray. Some
CD-writers do not refresh the CD contents after writing and thus falsely assume
that the just written CD is still empty. Those burners have to be forced to do a
refresh by opening and closing the tray.
 |
Go to the Options
dialog for your drive by choosing Drive Options... from the EAC menu
or press F10.
Click OK to pass the warning message that may appear. If the
drive you know the read offset of is
different from the drive you wrote the offset test CD with, do not forget to
change EAC to that drive. You can change the drive in the top left drop down box
as seen before. In our example here we use the Plextor PlexWriter PX-R820Ti for
writing and a Plextor UltraPlex PX-32TSi for reading. Earlier the read offset
of the UltraPlex 32x was determined so we will do the new read offset
detection with this drive.
On the Offset / Speed tab click the Detect read sample offset correction...
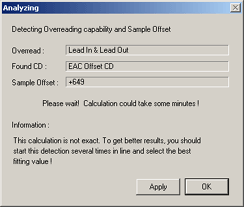
button. A dialog box Analyzing will popup showing the status
of the read offset detection process. First thing that's detected is whether or not
the drive is capable of overreading into the Lead-In and/or Lead-Out, but for
some reasons this information is not always reliable when tested with an EAC
offset test CD. Thus only trust the information you got with a pressed CD.
After the read offset detection finished EAC returns the
detected sample offset. Do not apply this value! You already
have the correct read offset. We only need this detected sample
offset to calculate the write offset. The sample
offset Exact Audio Copy returns is also called the combined read/write offset correction
and it represents the total offset of your writer and
reader combination. If you use another program for writing than EAC you should
use this combined read/write offset correction for reading audio CDs.
More about that later. To calculate the write offset:
write offset = combined read/write offset correction - read offset correction = 649 - 679 = -30
Thus the write offset of the PlexWriter 8/20 is -30
samples. You should enter this value in the write samples offset
field on the Writer tab of the Options
dialog for your CD-writer. Click the OK button to save the
settings. You are now able to make 100% offset corrected duplicates of audio
CDs!
If you not already did, read The
Truth About Offsets to find out why it is sometimes impossible to have a
100% perfect duplicate of a CD, even when using offset correction. The problem
is the overwriting capability of the CD-recorder. If the drive is not able to
overwrite into the Lead-In (actually, it's the pregap of the CD - for a positive
write offset) or overwrite into the Lead-Out (for a negative write offset)
there will always be missing samples at the beginning or end of the copied CD
respectively.
Again, like said in The
Truth About Offsets this is such a small time it may be ignored.
|